French Political Hierarchy: Understanding the Structure and Power Dynamics
Greetings, Readers! In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the French political hierarchy, providing you with valuable insights into its structure, functions, and significance. As one of the oldest democracies in the world, France boasts a unique political system that has evolved over centuries. By understanding the French political hierarchy, you will gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s governance and power dynamics. So, let’s dive right in!
Introduction
The French political hierarchy is a complex system that encompasses various branches of government and administrative bodies. It is essential to comprehend this hierarchy to grasp how power is distributed and decisions are made in the country. In this section, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the French political hierarchy, exploring its key components and their roles.
1. The President of the French Republic: 🏛️
The President holds the highest office in the French political hierarchy. Elected by popular vote for a five-year term, the President represents the nation both domestically and internationally. They play a crucial role in shaping policies, appointing government officials, and ensuring the proper functioning of the state.
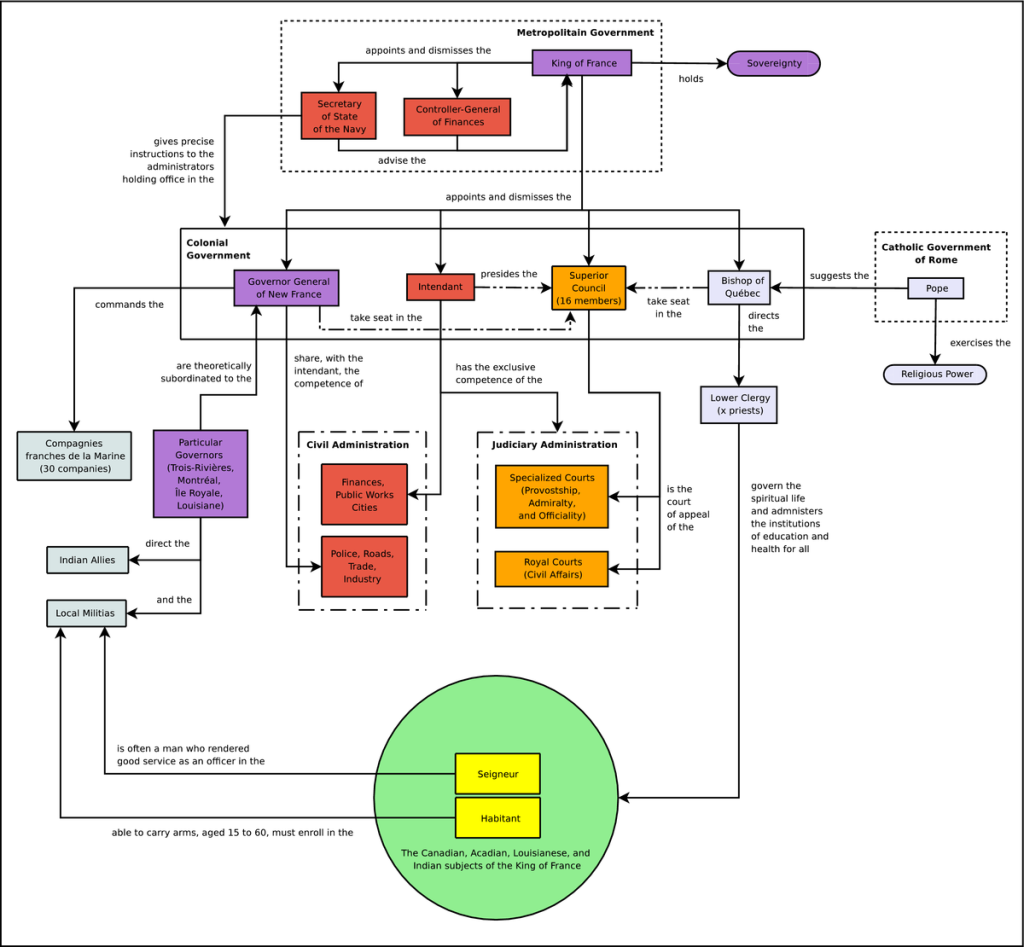
Image Source: wikimedia.org
2. The Prime Minister: 🎩
The Prime Minister is appointed by the President and serves as the head of the government. They are responsible for implementing policies, managing ministries, and representing the government in the National Assembly. The Prime Minister works closely with the President to drive the country’s agenda.
3. The National Assembly: 🏛️🗳️
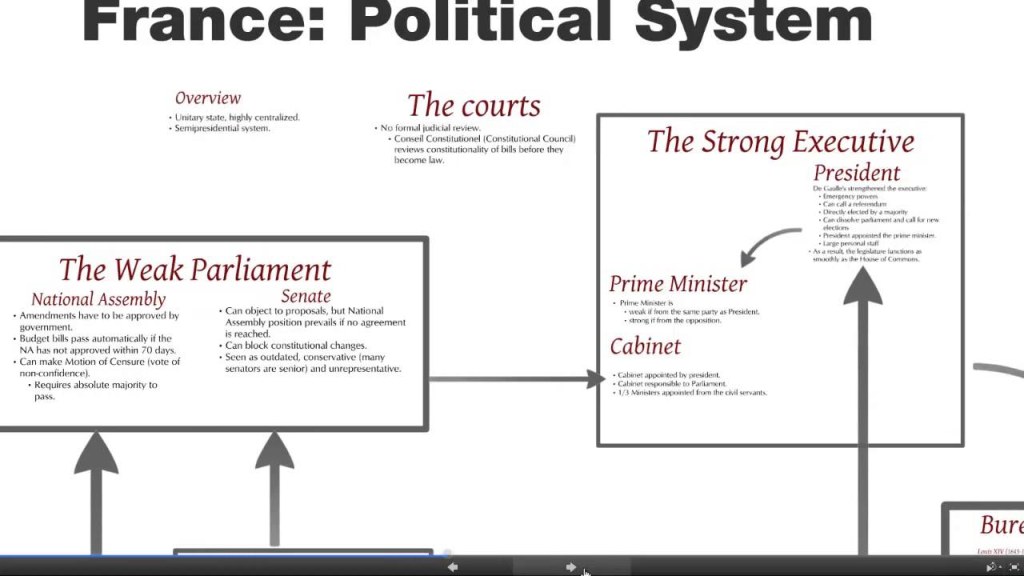
Image Source: ytimg.com
The National Assembly is the lower house of the French parliament. Its members, known as deputies, are elected by the public through direct voting. The National Assembly holds legislative power, enacting laws, scrutinizing the government’s actions, and representing citizens’ interests.
4. The Senate: 🏛️🗳️
The Senate is the upper house of the French parliament. Its members, called senators, are elected indirectly by an electoral college. The Senate acts as a revising chamber, examining laws proposed by the National Assembly and providing a platform for regional and local interests.
5. The Constitutional Council: ⚖️
The Constitutional Council ensures the constitutionality of laws and regulations. Comprising nine members, including former Presidents and appointed experts, the council reviews legislation before it is enacted. It safeguards the democratic principles and constitutional rights of French citizens.
6. The Council of State: ⚖️
The Council of State acts as France’s highest administrative court. It provides legal advice to the government, settles administrative disputes, and ensures the legality of administrative decisions. The council serves as an essential pillar of the French political and legal system.
What is the French political hierarchy?
The French political hierarchy refers to the system of government and administrative bodies that govern the country. It comprises various institutions, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
Who holds the highest office in the French political hierarchy?
The highest office in the French political hierarchy is held by the President of the French Republic. Elected by the people, the President represents the nation and plays a vital role in decision-making and governance.
When was the French political hierarchy established?
The French political hierarchy has evolved over centuries, with its roots dating back to the establishment of the French monarchy in the Middle Ages. However, the current political structure took shape after the French Revolution in 1789, which led to the establishment of the First French Republic.
Where does the French political hierarchy derive its power?
The power of the French political hierarchy is derived from the constitution, which outlines the roles, responsibilities, and limitations of each branch of government. The constitution serves as the foundation of the French political system.
Why is understanding the French political hierarchy important?
Understanding the French political hierarchy is crucial for citizens and policymakers alike. It enables citizens to participate in the democratic process, hold their representatives accountable, and make informed decisions. For policymakers, a deep understanding of the hierarchy facilitates effective governance and decision-making.
How does the French political hierarchy function?
The French political hierarchy functions through a system of checks and balances, ensuring that power is not concentrated in one branch or individual. The President, Prime Minister, parliament, and other institutions work together to make and implement decisions, ensuring the smooth functioning of the government and safeguarding democracy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the French Political Hierarchy
Like any political system, the French political hierarchy has its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore them in detail:
Advantages:
1. Stability: The French political hierarchy provides a stable framework for governance, ensuring continuity in decision-making and policy implementation.
2. Representation: The National Assembly and Senate represent citizens’ interests, providing a platform for diverse voices and opinions.
3. Separation of Powers: The division of powers between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches prevents the concentration of power in a single entity, fostering accountability and democracy.
Disadvantages:
1. Slow Decision-Making: The multi-layered nature of the French political hierarchy can lead to delays in decision-making, hindering rapid responses to emerging issues.
2. Complex Coordination: The collaboration between the President, Prime Minister, and various government bodies can be challenging, potentially resulting in coordination issues.
3. Electoral Challenges: The indirect election of senators and the complexities of the electoral system can sometimes lead to a disconnect between citizens’ choices and the composition of the Senate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Q: How often are presidential elections held in France?
A: Presidential elections in France are held every five years.
2. Q: Can the President serve more than one term?
A: Yes, the President can serve up to two consecutive five-year terms.
3. Q: How are members of the National Assembly elected?
A: Members of the National Assembly are elected through direct voting by the public.
4. Q: How do the National Assembly and Senate collaborate?
A: Both chambers collaborate to draft and pass legislation. However, the National Assembly has the final say in case of disagreements.
5. Q: Can the Prime Minister be from a different political party than the President?
A: Yes, the President can appoint a Prime Minister from a different political party. This can lead to a cohabitation scenario, where the President and Prime Minister represent different political ideologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the French political hierarchy is essential for comprehending the country’s governance and power dynamics. From the President’s role at the pinnacle of the hierarchy to the legislative powers of the National Assembly and Senate, each component plays a significant role in shaping France’s political landscape. By grasping the advantages, disadvantages, and functioning of this hierarchy, citizens and policymakers can actively participate in the democratic process and contribute to the nation’s progress.
Final Remarks
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute legal advice or reflect the views of any specific organization or institution. The French political hierarchy is subject to change, and readers are encouraged to refer to official sources for the most up-to-date information.