French Political Symbols: A Journey Through History
Greetings, friends! Today, we embark on a fascinating exploration of French political symbols. From the iconic Marianne to the tricolor flag, these symbols have played a crucial role in shaping the nation’s history and political landscape. Join us as we delve into the meaning, significance, and evolution of these powerful emblems.
Introduction
France, known for its rich history and cultural heritage, has a long-standing tradition of political symbolism. These symbols represent the ideals, values, and aspirations of the French people. They serve as potent reminders of the struggles, triumphs, and collective identity of the nation.
In this article, we will discuss the various political symbols that have emerged throughout French history. We will uncover their origins, explore their meaning, and examine their continued relevance in contemporary society. Join us on this enlightening journey through the intricate tapestry of French political symbols.
The Tricolor Flag: A Unifying Emblem
🇫🇷 The tricolor flag, consisting of blue, white, and red vertical stripes, is one of the most recognizable symbols of France. It represents the values of the French Revolution – liberty, equality, and fraternity. The blue symbolizes freedom, the white stands for equality, and the red represents fraternity. This iconic flag has become a unifying emblem for the French people, transcending political boundaries.
Historical Context
The tricolor flag was first introduced during the French Revolution in 1789. It replaced the royal white flag, which symbolized the monarchy. The adoption of the tricolor flag marked a significant shift in power and ideology, signaling the birth of a new era in French history. Since then, it has remained a symbol of national pride and unity.
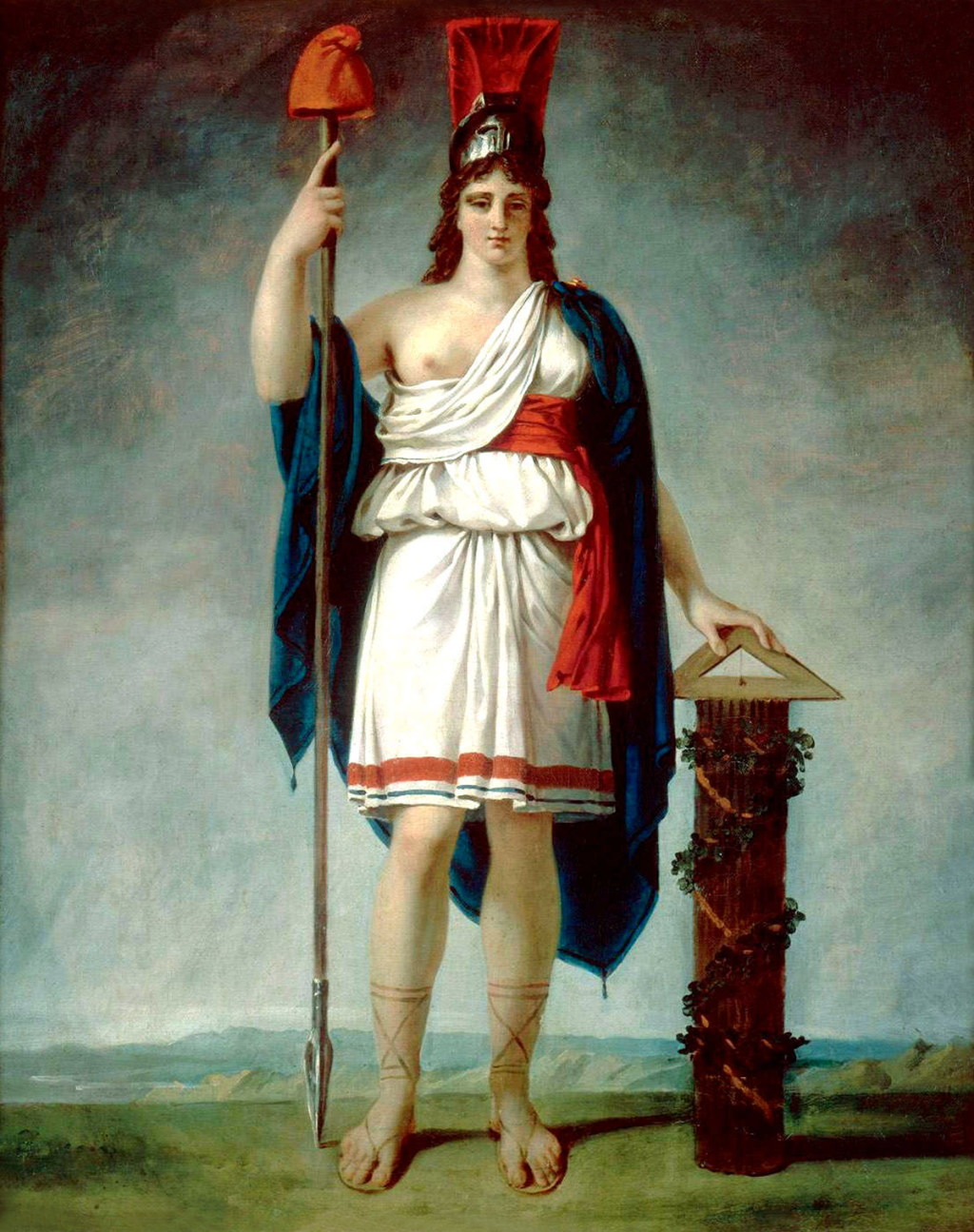

Image Source: wikimedia.org
Throughout the years, the tricolor flag has been proudly displayed during significant historical events such as the French Revolution, the July Revolution, and both World Wars. It has become a poignant reminder of the French people’s resilience and their enduring commitment to the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Contemporary Significance
Today, the tricolor flag continues to hold immense significance in French society. It is prominently displayed during national holidays, sporting events, and political rallies. The flag serves as a unifying symbol, bringing together individuals from diverse backgrounds under a shared sense of national identity. It represents the values that France stands for and serves as a reminder of the nation’s commitment to liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Marianne: The Symbol of Liberty
🗽 Marianne, the personification of the French Republic, is another iconic political symbol deeply rooted in French history. She is often depicted as a young woman wearing a Phrygian cap and holding a spear or a torch. Marianne represents liberty, reason, and the triumph of the French people over oppression.
Origins and Evolution
The origins of Marianne can be traced back to ancient Roman times, where she represented the goddess of liberty. However, it was during the French Revolution that Marianne became the symbol of the Republic. Her image was popularized through various artworks, sculptures, and political propaganda, reinforcing the ideals of the Revolution.
Over the years, Marianne’s portrayal has evolved to reflect the changing values and aspirations of French society. She has been depicted in various styles, ranging from classical to modernist, and is often seen as a representation of the prevailing political and social climate.
Symbolism and Meaning
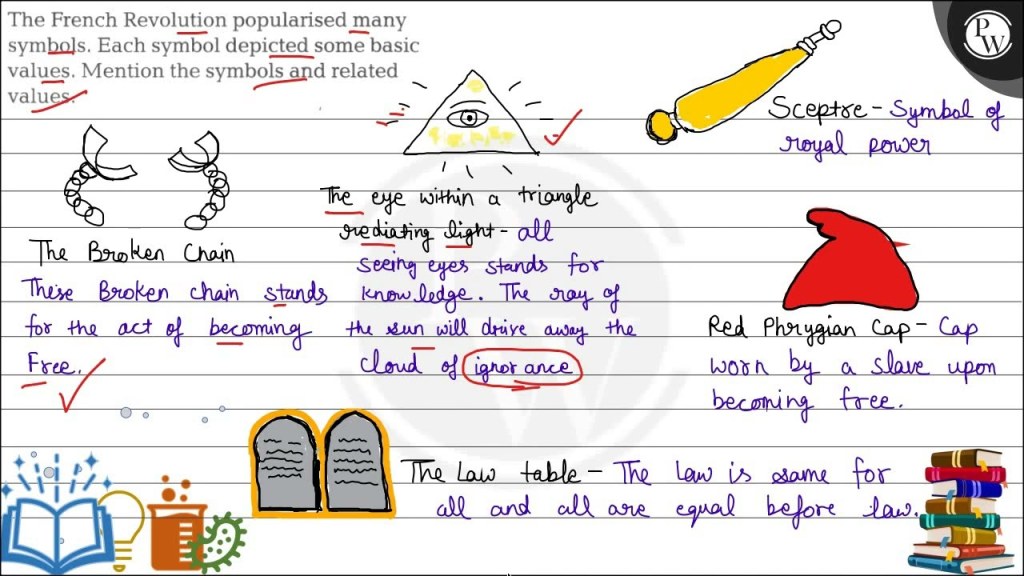
Image Source: ytimg.com
Marianne embodies the French people’s struggle for liberty and equality. Her Phrygian cap, a symbol of freed slaves in ancient Rome, represents the emancipation from tyranny. The torch she holds symbolizes enlightenment and the spreading of knowledge. Marianne’s image serves as a constant reminder of the democratic principles that form the foundation of the French Republic.
What Are French Political Symbols?
🎭 French political symbols are visual representations that encapsulate the values, beliefs, and aspirations of the French people. These symbols serve as powerful tools for political communication, rallying support, and uniting the nation. They are deeply ingrained in French history and culture, reflecting the country’s political evolution over the centuries.
The Significance of Political Symbols
Political symbols play a vital role in shaping public perception and mobilizing individuals towards a common cause. They serve as tangible representations of intangible concepts, making complex ideologies accessible and easily understood. By encapsulating the spirit of a movement or ideology, political symbols evoke emotions, foster solidarity, and inspire action.
The Evolution of French Political Symbols
French political symbols have evolved alongside the country’s political landscape. From the fleur-de-lis, a symbol of the monarchy, to the tricolor flag of the Revolution, these symbols have reflected the shifting power dynamics and prevailing ideologies throughout French history. They have provided a visual language through which political movements and ideologies can be expressed.
The Role of French Political Symbols Today
In contemporary France, political symbols continue to play a significant role in political discourse and national identity. They are visible during elections, protests, and official ceremonies, serving as a reminder of the nation’s history, values, and aspirations. These symbols foster a sense of collective identity and inspire citizens to actively engage in the political process.
Who Uses French Political Symbols?

Image Source: z-dn.net
👥 French political symbols are utilized by a wide range of individuals and groups, from political parties to grassroots movements. They serve as a means of identification, expressing a shared set of values, beliefs, and goals.
Political Parties
French political parties often adopt specific symbols to rally support and distinguish themselves from their competitors. These symbols can range from animals and plants to abstract representations of their ideologies. For example, the Socialist Party uses a rose as its symbol, representing the party’s commitment to social justice and equality.
Protest Movements
Protest movements in France have also utilized political symbols to convey their messages and mobilize supporters. These symbols are often associated with specific causes or ideologies. For instance, the yellow vest movement, which protested against economic inequality, adopted the yellow vest as its symbol, representing the struggles of working-class individuals.
The General Public
The general public in France also embraces political symbols as a way to express their support for certain ideologies or causes. Individuals may wear badges, display flags, or use symbols in their social media profiles to signify their alignment with a particular political movement or party.
When Did French Political Symbols Emerge?
⏳ French political symbols have a long history, dating back to ancient times. However, it was during the French Revolution in the late 18th century that political symbols gained significant prominence and began to shape the nation’s political landscape.
The French Revolution
The French Revolution, which began in 1789, marked a turning point in French history and the emergence of powerful political symbols. The revolutionaries sought to overthrow the monarchy and establish a democratic republic, and symbols became a critical tool for conveying their ideals and rallying support.
Adoption of the Tricolor Flag
During the French Revolution, the tricolor flag was officially adopted as the national flag of France. It represented the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity – core tenets of the revolutionaries’ vision for a new society. The adoption of the tricolor flag signaled a break from the past and the birth of a new era.
Symbolic Art and Propaganda
Artists and political propagandists played a crucial role in popularizing political symbols during the French Revolution. They created powerful images and artworks that depicted the ideals of the revolution, such as the iconic image of Marianne. These visual representations became instrumental in shaping public opinion and garnering support for the revolutionary cause.
Where Are French Political Symbols Found?
📍 French political symbols can be found in various contexts and locations, serving as reminders of the nation’s history, values, and aspirations. From public spaces to political rallies, these symbols are woven into the fabric of French society.
Public Buildings and Monuments
French political symbols are often prominently displayed on public buildings and monuments. For example, the tricolor flag can be seen flying proudly atop government buildings, schools, and historical sites. Marianne’s image adorns numerous public monuments and serves as a symbol of the French Republic.
National Holidays and Events
Political symbols take center stage during national holidays and events in France. The tricolor flag is unfurled during Bastille Day celebrations, commemorating the storming of the Bastille and the beginning of the French Revolution. These occasions provide an opportunity for the nation to come together and reaffirm its commitment to the values represented by these symbols.
Political Rallies and Protests
French political symbols are a common sight at political rallies and protests. Supporters of different parties and movements proudly display symbols, banners, and flags representing their ideologies. These symbols serve as a visual representation of collective identity and the shared goals of the participants.
Why Are French Political Symbols Significant?
❓ French political symbols hold immense significance due to their ability to evoke emotions, foster solidarity, and inspire action. They represent the ideals, values, and aspirations of the French people and serve as powerful tools for political communication and mobilization.
Visual Representation of Ideals
Political symbols provide a visual representation of complex ideals and concepts, making them accessible and relatable to a broad audience. They distill complex ideologies into easily recognizable images, enabling individuals to connect emotionally and intellectually with the underlying principles.
Fostering National Identity
French political symbols foster a sense of national identity and solidarity. They remind individuals of their shared history, values, and aspirations. These symbols transcend political divisions and unite the nation under a common banner, reinforcing the bonds that hold French society together.
Inspiring Political Engagement
Political symbols serve as catalysts for political engagement and action. They can inspire individuals to actively participate in the political process, whether through voting, protests, or joining political movements. These symbols motivate citizens to fight for the principles they represent and work towards a better future.
How Do French Political Symbols Impact Society?
💼 French political symbols have a profound impact on society, shaping public discourse, influencing political decisions, and fostering a sense of collective identity. They serve as powerful tools for political communication, rallying support, and inspiring change.
Shaping Public Discourse
French political symbols shape public discourse by providing a visual language through which complex political ideologies and movements can be understood and debated. They frame the narrative and set the agenda, influencing public opinion and guiding discussions on key issues.
Influencing Political Decisions
Political symbols play a crucial role in influencing political decisions. They serve as rallying points for supporters, indicating shared values and goals. Political leaders and parties often leverage these symbols to strengthen their message, mobilize their base, and appeal to undecided voters.
Fostering Collective Identity
French political symbols foster a sense of collective identity and belonging. They unite individuals under a shared set of values and aspirations, transcending political affiliations. These symbols create a sense of community and solidarity, reinforcing the idea that the French people are bound together by a common purpose.
Advantages and Disadvantages of French Political Symbols
Advantages
1. Unity and Solidarity: Political symbols foster a sense of unity and solidarity among the French people, providing a common ground for diverse individuals to come together.
2. Communication and Mobilization: These symbols serve as powerful tools for political communication, mobilizing support, and inspiring action.
3. Historical Continuity: Political symbols connect the present with the past, reminding individuals of their shared history and values.
4. Emotional Connection: Symbols evoke emotions and create a personal connection with individuals, motivating them to engage in the political process.
5. Visual Representation: Political symbols distill complex ideologies into easily recognizable images, making them accessible to a broad audience.
Disadvantages
1. Divisiveness: Political symbols can sometimes exacerbate divisions within society, reinforcing political polarization and ideological conflicts.
2. Simplification of Complex Issues: Symbols may oversimplify complex political issues, leading to a superficial understanding of the underlying problems.
3. Manipulation and Propaganda: Symbols can be manipulated for political gain, distorting their original meaning and intent.
4. Exclusionary Nature: Political symbols may exclude individuals who do not identify with or subscribe to the ideologies they represent.
5. Limited Scope: Symbols can only convey a limited amount of information and may fail to capture the nuances and complexities of political ideologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Are French political symbols protected by law?
A1: Yes, French political symbols, including the tricolor flag and Marianne, are protected by law. Their usage is regulated to ensure their appropriate representation and prevent misuse.
Q2: Who designed the current version of Marianne?
A2: The current version of Marianne was designed by the French sculptor, Olivier Doaré. His design was selected through a national competition organized by the French government.
Q3: Can individuals use French political symbols for personal purposes?
A3: Yes, individuals are free to use French political symbols for personal purposes, such as displaying the tricolor flag or wearing symbols associated