French Politics Explained Simply
Welcome, friends! In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of French politics and provide a simplified understanding of this complex subject. France, known for its rich history and influential role in European affairs, has a political system that may seem daunting at first glance. However, by breaking it down into digestible pieces, we hope to make it easier for you to comprehend. So, let’s dive in!
Introduction
French politics encompasses the political institutions, ideologies, and processes that shape the governance of the French Republic. As a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, France has a unique political system that combines elements of both presidential and parliamentary systems.
The French political landscape is characterized by a multi-party system, with parties falling across the political spectrum. The major political parties include La République En Marche! (LREM), Les Républicains (LR), the Socialist Party (PS), and the National Rally (RN). Understanding the nuances of French politics is essential to grasp the country’s decision-making processes and policies.
Now, let’s explore the key components of French politics in greater detail:
What is French Politics?
At its core, French politics refers to the way power is exercised and managed within the French Republic. It encompasses the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, as well as the political parties, interest groups, and public opinion that shape the decision-making process.

Image Source: wikimedia.org
French politics is marked by a separation of powers, whereby the President of the Republic represents the executive branch, while the Parliament (comprising the National Assembly and the Senate) represents the legislative branch. The Constitutional Council serves as the guardian of the French Constitution and ensures its compliance with the law.
French Politics at a Glance:
✅ Semi-presidential representative democratic republic
✅ Multi-party system
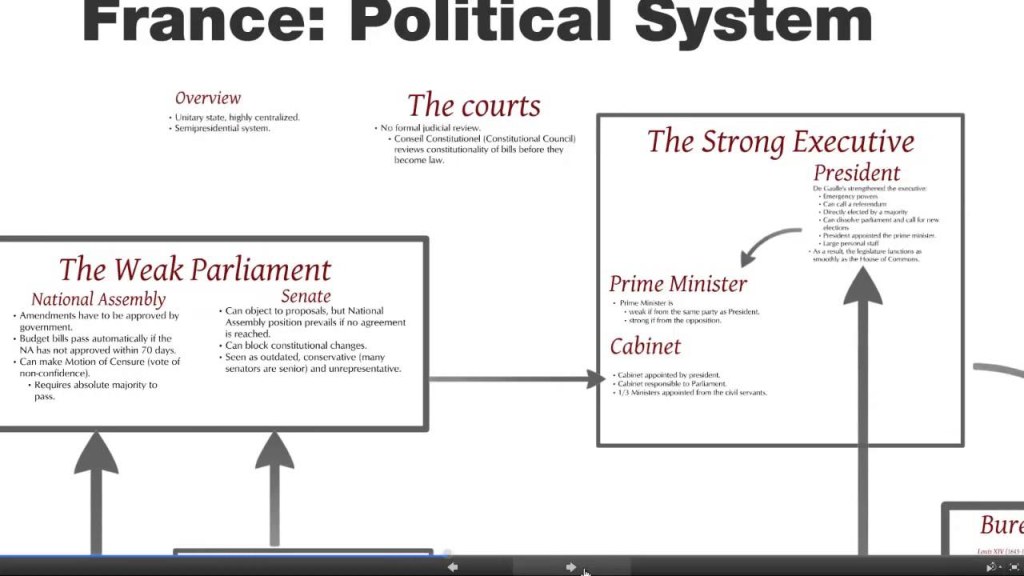
Image Source: ytimg.com
✅ Separation of powers
✅ Executive: President of the Republic
✅ Legislative: National Assembly and Senate

Image Source: expatica.com
✅ Judicial: Constitutional Council
Who are the Key Players?
In French politics, several prominent figures play pivotal roles in governance and decision-making. The President of the Republic, as the head of state, holds significant influence. They are elected to a five-year term and appoint the Prime Minister, who leads the government.
The French Parliament consists of two chambers: the National Assembly and the Senate. Members of Parliament, known as deputies and senators respectively, are elected by the people. They propose and vote on laws, scrutinize the government’s actions, and represent the interests of their constituents.
Political parties also play a crucial role in French politics. They offer different ideologies and policies, competing for electoral support and influencing political outcomes.
Key Players in French Politics:
✅ President of the Republic
✅ Prime Minister
✅ Members of Parliament
✅ Political Parties
When are French Elections Held?
In France, elections are held regularly to elect representatives at various levels of government. Presidential elections take place every five years, with the most recent one occurring in 2017. Parliamentary elections, which determine the composition of the National Assembly, are held shortly after the presidential elections.
Local elections, including municipal and regional elections, are held every six years. These elections allow citizens to choose their local representatives, mayors, and regional councilors.
French Election Cycle:
✅ Presidential elections: every five years
✅ Parliamentary elections: shortly after presidential elections
✅ Local elections: every six years
Where does Power Lie?
In the French political system, power is distributed among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The President of the Republic, as the head of state, wields significant influence over foreign policy, defense, and appointment of government officials.
The Parliament, comprising the National Assembly and the Senate, holds legislative power. It debates and passes laws, oversees the government’s actions, and represents the interests of the French people.
The Constitutional Council ensures the constitutionality of laws and has the authority to strike down legislation that violates constitutional principles.
Why is French Politics Significant?
Understanding French politics is crucial due to France’s influential role in European and global affairs. As one of the world’s leading economies and a founding member of the European Union, France’s political decisions and policies have far-reaching consequences.
French politics also shape domestic policies, such as healthcare, education, and social welfare. By staying informed about French politics, individuals can better understand the factors that contribute to the country’s social, economic, and cultural development.
How Does French Politics Work?
The French political system operates through a series of checks and balances. The President of the Republic, elected by the people, appoints the Prime Minister, who forms the government. The government is accountable to the Parliament, which holds the power to pass or reject legislation proposed by the executive.
Political parties play a pivotal role in French politics by advocating for their policy platforms and competing for electoral support. They influence policy decisions through parliamentary debates, public campaigns, and grassroots activism.
Key Features of French Politics:
✅ Checks and balances
✅ President appoints the Prime Minister
✅ Government accountable to Parliament
✅ Political parties influence policy decisions
Advantages and Disadvantages of French Politics
Like any political system, French politics has its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore some of these pros and cons:
Advantages:
1️⃣ Stability: The semi-presidential system provides stability by balancing power between the President and the Prime Minister.
2️⃣ Representation: The multi-party system ensures diverse representation and allows for a range of policy perspectives.
3️⃣ Checks and Balances: The separation of powers prevents any one branch from becoming too dominant and safeguards against abuses of power.
Disadvantages:
1️⃣ Political Fragmentation: The presence of multiple political parties can lead to coalition governments and potential policy gridlock.
2️⃣ Slow Decision-Making: The need to build consensus among different parties can slow down the legislative process.
3️⃣ Limited Presidential Power: The President’s power is somewhat constrained by the Prime Minister and the Parliament.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the role of the President of the Republic?
The President of the Republic serves as the head of state and represents France domestically and internationally. They are responsible for appointing the Prime Minister, leading the executive branch, and making decisions on national security and foreign policy.
2. How are political parties formed in France?
Political parties in France are formed through grassroots organizing, ideological alignment, and registration with the Ministry of the Interior. They develop policy platforms, nominate candidates for elections, and engage in political campaigns to gain support from the electorate.
3. How does the French electoral system work?
The French electoral system combines elements of proportional representation and majority voting. Presidential elections use a two-round system, ensuring that the winner receives an absolute majority of votes. Parliamentary elections employ a two-round system in single-member constituencies, with additional seats allocated through proportional representation.
4. What are some of the major political parties in France?
Some of the major political parties in France include La République En Marche! (LREM), Les Républicains (LR), the Socialist Party (PS), the National Rally (RN), and France Insoumise.
5. How do French citizens participate in the political process?
French citizens participate in the political process through voting in elections, joining political parties, engaging in grassroots activism, and participating in public debates. They can also contact their elected representatives to voice their opinions and concerns.
Conclusion
French politics is a complex yet fascinating subject that plays a vital role in shaping the country’s direction and influencing global affairs. By understanding the key players, electoral processes, and advantages and disadvantages of the French political system, individuals can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of governance in France.
We encourage you to stay informed, engage in political discourse, and exercise your democratic rights. Together, we can contribute to a better understanding of French politics and work towards a more inclusive and prosperous future.
Final Remarks
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as professional advice. The political landscape in France is subject to change, and readers are encouraged to seek current and accurate information from reputable sources.