French Politics 101: Understanding the Key Aspects of the French Political System
Introduction
Dear Readers,
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on French politics. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the French political system, providing you with a detailed overview. Whether you are a political enthusiast or simply curious about the subject, this article will equip you with the necessary knowledge to understand the ins and outs of French politics.
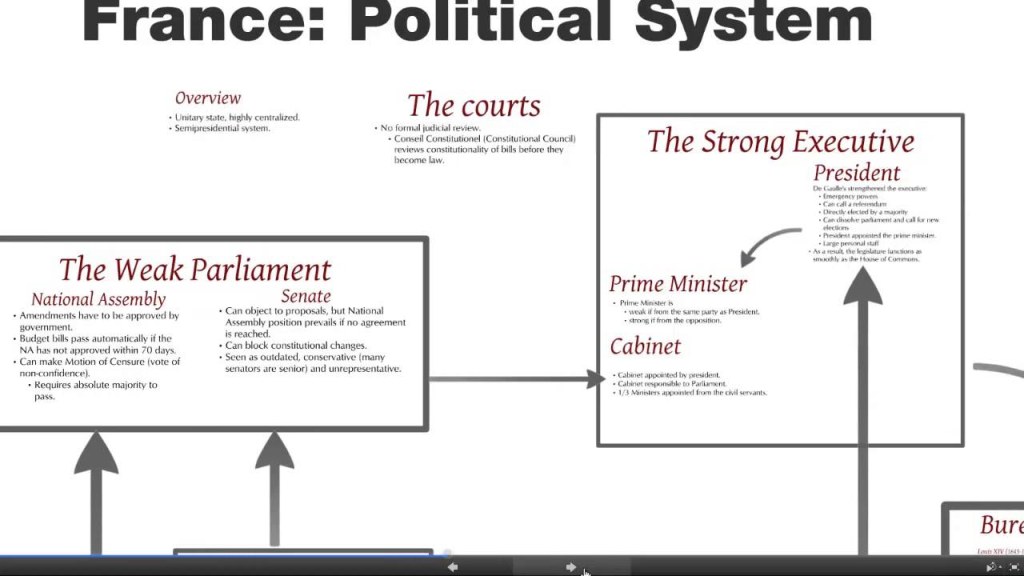
Image Source: ytimg.com
So, let us embark on this journey to explore the fascinating world of French politics and gain a deeper understanding of its key aspects.
What is French Politics?
📌 French politics refers to the governance, political activities, and power dynamics within the French Republic. It encompasses various institutions, parties, and ideologies that shape the country’s political landscape.
Fundamentally, French politics revolves around the principles of democracy, equality, and secularism. The political system in France is characterized by a semi-presidential form of government, which combines elements of both a presidential and parliamentary system.
To comprehend French politics, it is essential to familiarize ourselves with its key players, historical context, and governing structures.
Key Players in French Politics
📌 French politics involves several key players who drive the decision-making process and shape the country’s political landscape. These players include:
1. President of the French Republic: The president is the head of state and wields significant executive powers.
2. Prime Minister: The prime minister is appointed by the president and leads the government.
3. Members of Parliament: France has a bicameral legislature consisting of the National Assembly and the Senate.
4. Political Parties: Numerous political parties play a crucial role in French politics, representing diverse ideologies and interests.
5. Interest Groups: These organizations advocate for specific causes and exert influence on political decision-making.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the key players, let’s explore the historical context of French politics.
Historical Context of French Politics
📌 Understanding the historical context is crucial to comprehend the evolution and current state of French politics. The roots of French politics can be traced back to the French Revolution in the late 18th century, which led to the establishment of a democratic framework.
Over the years, France has experienced various political regimes, including monarchies, republics, and authoritarian regimes. These historical events have shaped the French political culture, emphasizing values such as liberty, equality, and fraternity.
The establishment of the French Fifth Republic in 1958 marked a significant turning point in French politics and introduced the semi-presidential system that is in place today.
Now that we have explored the historical context, let’s delve into the functioning of the French political system.
Functioning of the French Political System
📌 The French political system operates within a framework defined by the Constitution of the Fifth Republic. It is a system of checks and balances that ensures the separation of powers between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The president, as the head of state, represents the nation both domestically and internationally. The prime minister, appointed by the president, leads the government and is responsible for implementing policies.
The French Parliament consists of the National Assembly and the Senate. The National Assembly, with 577 members, initiates and votes on legislation, while the Senate, with 348 members, reviews and revises proposed laws.
Political parties play a vital role in the French political system. They compete in elections, form coalitions, and articulate their visions and policy proposals to address societal challenges.
Additionally, interest groups, such as trade unions and professional associations, have a significant influence on shaping policies and advocating for specific interests.
Now that we have gained a broad understanding of French politics, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of the French political system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of French Politics
📌 Like any political system, the French political system has its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s examine both sides to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Advantages of French Politics
Advantage 1: Representation of Diverse Views
Advantage 2: Balance of Power
Advantage 3: Emphasis on Social Welfare
Advantage 4: Protection of Civil Liberties
Advantage 5: Influence on International Affairs
Disadvantages of French Politics
Disadvantage 1: Fragmented Political Landscape
Disadvantage 2: Slow Decision-Making Process
Disadvantage 3: Political Polarization
Disadvantage 4: Bureaucratic Challenges
Disadvantage 5: Potential for Populism
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is the French president elected directly by the people?
Answer: Yes, the French president is elected directly by the people through a two-round voting system.
2. What is the term duration for the French president?
Answer: The term duration for the French president is five years, with a maximum of two consecutive terms.
3. How many political parties are there in France?
Answer: France has numerous political parties, ranging from major ones to smaller niche parties.
4. What role do interest groups play in French politics?
Answer: Interest groups in France play a significant role in advocating for specific causes and influencing political decision-making.
5. Who was the longest-serving French president?
Answer: François Mitterrand holds the record for being the longest-serving French president, serving for 14 years from 1981 to 1995.
Conclusion: Your Role in Understanding French Politics
Dear Readers,
By familiarizing yourself with the key aspects of French politics, you become an informed citizen capable of actively participating in discussions and making informed decisions.
As the political landscape evolves and new challenges arise, it is essential to stay engaged, question the status quo, and contribute to the democratic process. Remember, understanding French politics empowers you to shape the future of your nation.
So, let us continue to explore and analyze the intricacies of French politics, contributing to a more inclusive and prosperous society.
Final Remarks
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. The content does not constitute legal or professional advice. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any agency or institution.
Remember to always consult with legal and political experts for specific advice related to French politics or any other subject matter.