French Political Beliefs: A Deep Dive into the Ideologies Shaping the Nation
Greetings, readers! Today, we embark on an exploration of French political beliefs, delving into the ideologies that have shaped the nation’s political landscape for centuries. France, known for its rich history and influential thinkers, has been a breeding ground for various political convictions. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of French political beliefs, shedding light on their origins, key figures, advantages and disadvantages, and more. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
Introduction
What Are French Political Beliefs?
Key Figures and Influencers
Historical Context
Geographical Factors
Advantages and Disadvantages
The Evolution of French Political Beliefs
FAQ
Conclusion
Final Remarks
Introduction
France, a country widely regarded as the birthplace of modern democracy, has witnessed the emergence of diverse political beliefs throughout its history. These beliefs reflect the values, aspirations, and concerns of its people, shaping the nation’s governance and policies. Understanding French political beliefs is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of its political system and the motivations behind key decisions. In this introduction, we will explore seven key aspects that underpin the foundation of French political beliefs.
The Republican Tradition 🗽
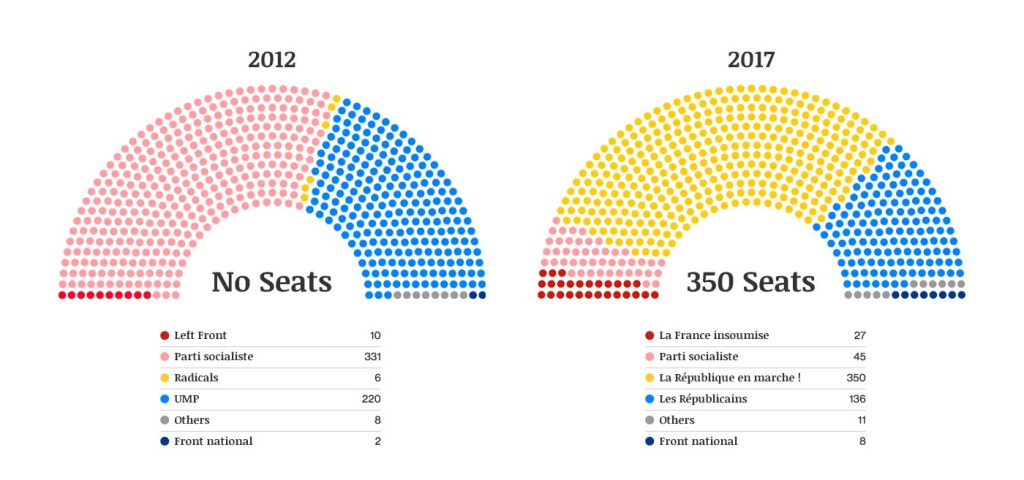
Image Source: cloudfront.net
At the heart of French political beliefs lies the republican tradition, which advocates for the establishment of a democratic and egalitarian society. Rooted in the Enlightenment era, this belief system upholds the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity, serving as the cornerstone of French political thought.
Secularism and Laïcité 🕊️
French political beliefs are deeply intertwined with secularism and the concept of laïcité. The French state, committed to the separation of church and state, maintains a strict secular stance. This principle, enshrined in the French Constitution, aims to ensure religious neutrality in public institutions and protect individual freedom of conscience.
Socialism and Social Democracy 🌹
France has a long-standing tradition of socialism and social democracy, which emphasizes social justice, welfare, and workers’ rights. Socialist parties and movements have played a significant role in shaping French politics, advocating for greater state intervention, progressive taxation, and the provision of public services.
Liberalism and Free-market Capitalism 💼
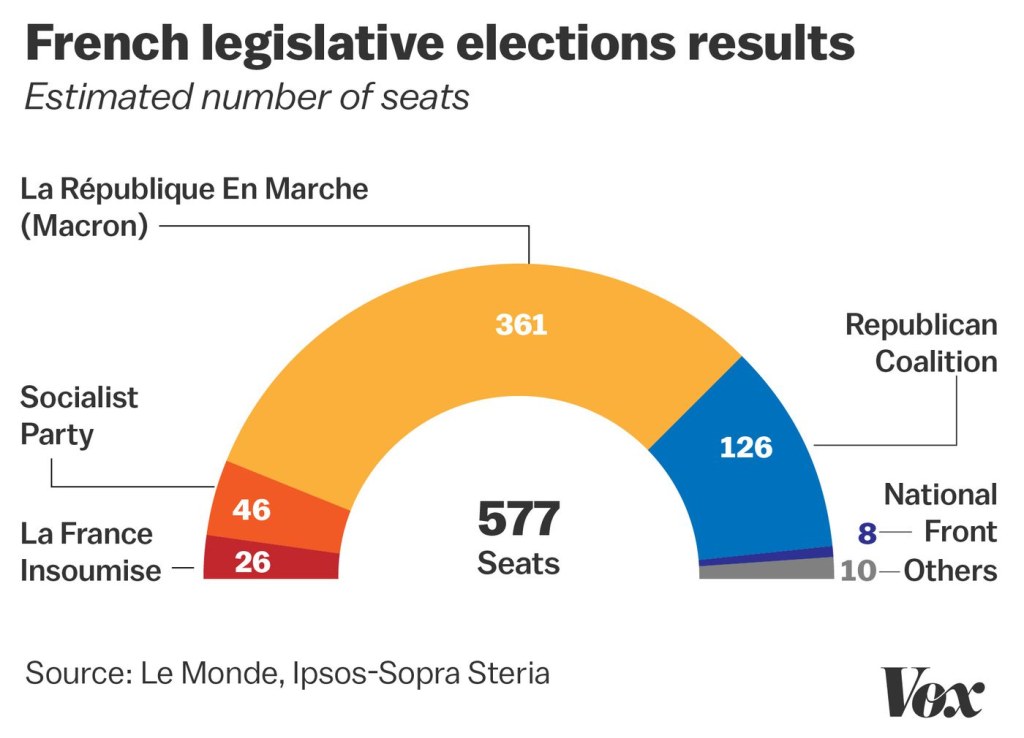
Image Source: vox-cdn.com
Liberalism and free-market capitalism also hold considerable sway in French political beliefs. These ideologies prioritize individual freedom, private property rights, and free trade. Liberal parties, such as the Radical Party and the Democratic Movement, champion economic liberalism, advocating for limited state intervention and deregulation.
Conservatism and Gaullism 🏰
Conservatism, particularly Gaullism, has been a prominent force in French politics since the mid-20th century. Gaullism, named after Charles de Gaulle, embodies a blend of conservative and nationalist ideas, emphasizing a strong executive, national sovereignty, and social cohesion. Conservative parties in France often espouse traditional values, such as family, order, and national identity.
Environmentalism and Green Politics 🌍

Image Source: wikimedia.org
Over the past few decades, environmentalism and green politics have gained traction in France. With growing concerns about climate change and sustainability, French political beliefs have seen the rise of green parties and movements, advocating for ecological responsibility, renewable energy, and environmental protection.
Far-right Nationalism and Populism 🤝
Lastly, French political beliefs are not immune to far-right nationalism and populism. This ideology, represented by parties like the National Front (now National Rally), emphasizes national identity, anti-immigration policies, and skepticism towards globalization. While far-right ideologies have faced significant opposition, they have left an indelible mark on French politics.
As we progress through this article, we will delve deeper into each aspect, shedding light on their historical context, key figures, advantages, and disadvantages. Stay tuned as we unravel the fascinating tapestry of French political beliefs!
What Are French Political Beliefs?
French political beliefs encompass a wide spectrum of ideologies, ranging from republicanism and socialism to liberalism and nationalism. These beliefs shape the nation’s political discourse, policies, and governance. Let’s explore each belief in more detail:
Republicansm
Republicanism lies at the core of French political beliefs. It advocates for a democratic society governed by elected representatives and upholds the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity. Republicans believe in protecting individual rights and fostering a sense of civic duty among citizens.
Socialism and Social Democracy
Socialism and social democracy in France emphasize social justice and equality. Socialist beliefs call for collective ownership of resources and the redistribution of wealth. Social democratic ideas, on the other hand, promote a mixed economy with a strong welfare state to ensure social welfare and mitigate inequality.
Liberalism
Liberalism, rooted in classical liberalism, prioritizes individual freedom, limited government intervention, and free-market capitalism. Liberals advocate for the protection of individual rights, economic freedom, and free trade.
Conservatism
Conservatism in France embraces traditional values, cultural heritage, and national identity. Supporters of conservatism often champion family values, order, and social cohesion. Gaullism, a prominent conservative ideology in France, emphasizes a strong executive and national sovereignty.
Green Politics
Green politics or environmentalism has gained prominence in recent years due to concerns about climate change and sustainability. Green parties advocate for environmental protection, renewable energy, and sustainable development.
Far-right Nationalism
Far-right nationalism, although controversial, has had an impact on French political beliefs. Parties with far-right ideologies promote nationalist sentiments, anti-immigration policies, and skepticism towards globalization. However, it’s crucial to note that far-right ideologies are met with significant opposition.
Key Figures and Influencers
Throughout French history, several influential figures have shaped the nation’s political beliefs. These individuals have left a lasting impact on French politics, ideologies, and governance. Let’s explore some of the key figures:
Charles de Gaulle 🎖️
Charles de Gaulle, a towering figure in French history, played a pivotal role in shaping French political beliefs. As the leader of the Free French Forces during World War II and the first President of the Fifth Republic, de Gaulle embodied Gaullism and emphasized national sovereignty, a strong executive, and social cohesion.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau 📚
Jean-Jacques Rousseau, an Enlightenment philosopher, greatly influenced French political beliefs with his work The Social Contract. Rousseau’s ideas on popular sovereignty, the general will, and the importance of a social contract laid the foundation for republican thought in France.
Karl Marx 🌍
While not French himself, Karl Marx’s Marxist theories had a profound impact on French socialism. Marx’s ideas on class struggle, communism, and the critique of capitalism influenced French socialist movements and the development of socialist and communist parties.
Simone Veil 🌸
Simone Veil, a French politician and feminist, played a crucial role in advancing women’s rights and reproductive rights in France. As the Minister of Health, Veil successfully advocated for the legalization of abortion in France, challenging prevailing conservative beliefs.
Dominique Voynet ☘️
Dominique Voynet, a prominent figure in French green politics, co-founded the French Green Party and served as the Minister of the Environment. Voynet’s environmental activism and advocacy for sustainable policies contributed to the rise of green politics in France.
Jean-Marie Le Pen 🤔
Jean-Marie Le Pen, the controversial founder of the National Front (now National Rally), represented far-right nationalism in French politics. His political career and nationalist rhetoric had a significant impact on French political beliefs, sparking debates and discussions on issues such as immigration and national identity.
These are just a few of the many influential figures who have shaped French political beliefs. Their contributions and ideologies continue to resonate in French society and politics today.
Historical Context
The development of French political beliefs is deeply rooted in the country’s historical context. Historical events and movements have shaped the ideologies and convictions that define French politics. Let’s explore some key moments in French history:
The French Revolution (1789-1799) 🎆
The French Revolution, a watershed moment in French history, laid the groundwork for many political beliefs that emerged afterward. The revolution’s ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity continue to influence French political thought, providing a foundation for republicanism and democratic principles.
The Commune of Paris (1871) 🏛️
The Paris Commune, a radical socialist and revolutionary government, briefly governed Paris in 1871. Although short-lived, the Commune left a lasting impact on French political beliefs, particularly socialist and communist ideologies. It highlighted the struggle for workers’ rights and the tension between the working class and the bourgeoisie.
World War II (1939-1945) 💣
World War II and the subsequent occupation of France by Nazi Germany had a profound impact on French political beliefs. The experience of occupation and resistance movements emphasized the importance of national unity, resistance against oppression, and the preservation of French identity.
May 1968 Protests 🌹
The May 1968 protests, a series of student-led uprisings and strikes, shook French society and had a significant impact on French political beliefs. The protests called for greater social and political reforms, such as increased workers’ rights, educational reforms, and a rejection of traditional values.
European Union Integration 🇪🇺
France’s involvement in the European Union (EU) and the process of European integration have also influenced French political beliefs. Debates surrounding national sovereignty, economic integration, and the balance between European cooperation and national interests have shaped the political landscape in France.
These historical events and movements have provided the backdrop for the evolution of French political beliefs, contributing to the diversity of ideologies and convictions present in the nation today.
Geographical Factors
The geographical factors of France have also influenced its political beliefs. The country’s diverse landscapes, regions, and urban-rural divide play a role in shaping political ideologies and priorities. Let’s explore some of these geographical factors:
Urban-Rural Divide 🏙️🌾
France’s urban-rural divide has implications for political beliefs. Urban areas, such as Paris and Lyon, tend to be more left-leaning, with a higher concentration of socialist and green parties. In contrast, rural areas often lean towards conservatism, emphasizing traditional values and national identity.
Regionalism and Cultural Identity 🗺️🎭
France’s regional diversity and cultural identities also influence political beliefs. Each region has its distinct traditions, dialects, and historical experiences, contributing to the diversity of political ideologies and priorities. Regionalist movements, such as those in Brittany and Corsica, advocate for greater regional autonomy and cultural preservation.
Overseas Territories and Global Influence 🌍🚩
France’s overseas territories, including French Guiana and Réunion, also play a role in shaping political beliefs. Issues of colonialism, immigration, and global influence are often prominent in political debates. The diverse cultures and histories of these territories contribute to the tapestry of political ideologies in France.
These geographical factors interplay with historical, social, and cultural contexts, contributing to the complex and diverse political beliefs found within France.
Advantages and Disadvantages
French political beliefs, like any ideological framework, have both advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore some of these advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of French Political Beliefs
Preservation of Democratic Principles 🗳️
French political beliefs, rooted in republicanism and democratic ideals, promote the preservation of democratic principles. The emphasis on liberty, equality, and fraternity ensures a system that values individual rights, social cohesion, and citizen participation in governance.
Social Welfare and Equality 🌹
French political beliefs, particularly socialist and social democratic ideologies, prioritize social welfare and equality. The emphasis on social justice, workers’ rights, and the provision of public services contributes to a more equitable society.
Environmental Responsibility 🌍
The rising influence of green politics in French political beliefs promotes environmental responsibility and sustainability. This emphasis on renewable energy, ecological preservation, and climate action contributes to the protection of the environment for future generations.